Watch these trees for Emerald Ash Borer
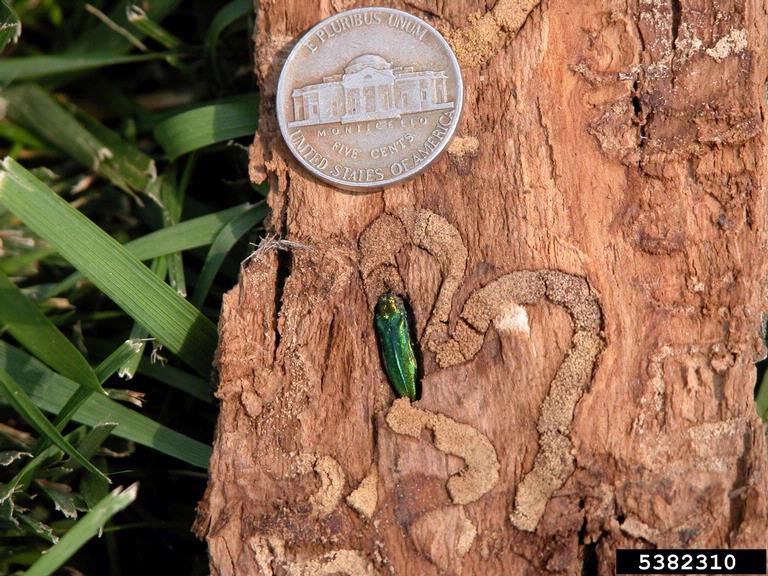
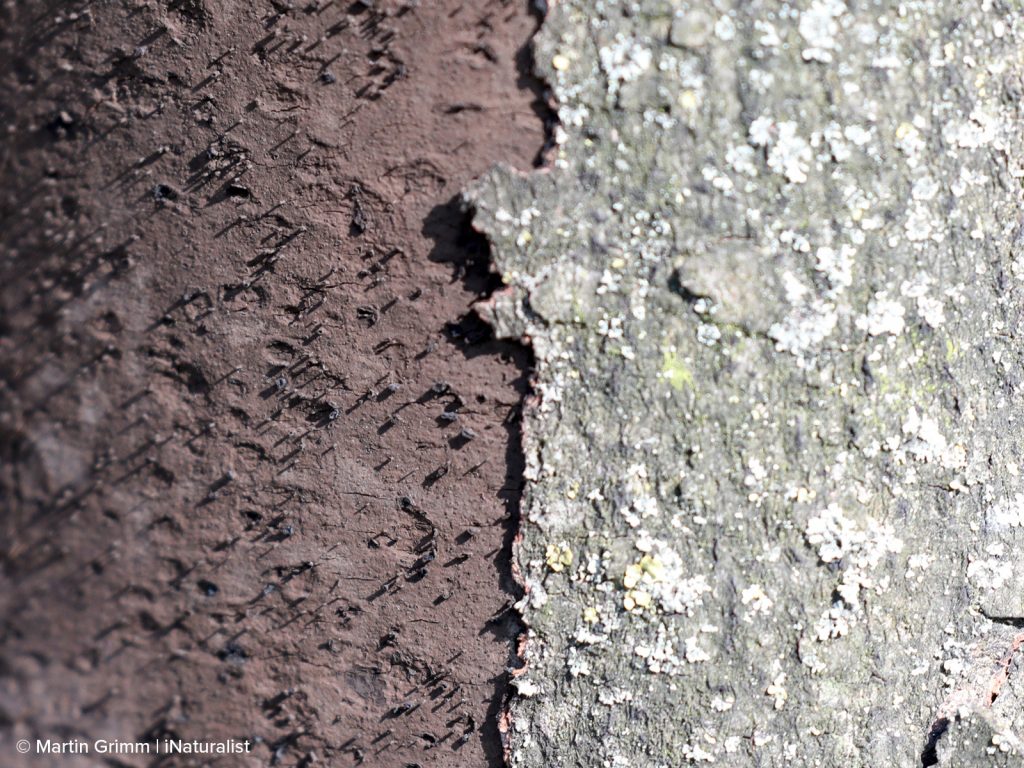
Emerald Ash Borer (EAB) is an invasive insect pest that has devastated populations of ash trees throughout the eastern US. Our local and endemic ash species, Oregon ash, is susceptible, but EAB has not been found on the West Coast yet. States need community scientists to keep an eye out and report concerns in order to respond quickly and reduce the impacts of the invasive EAB.
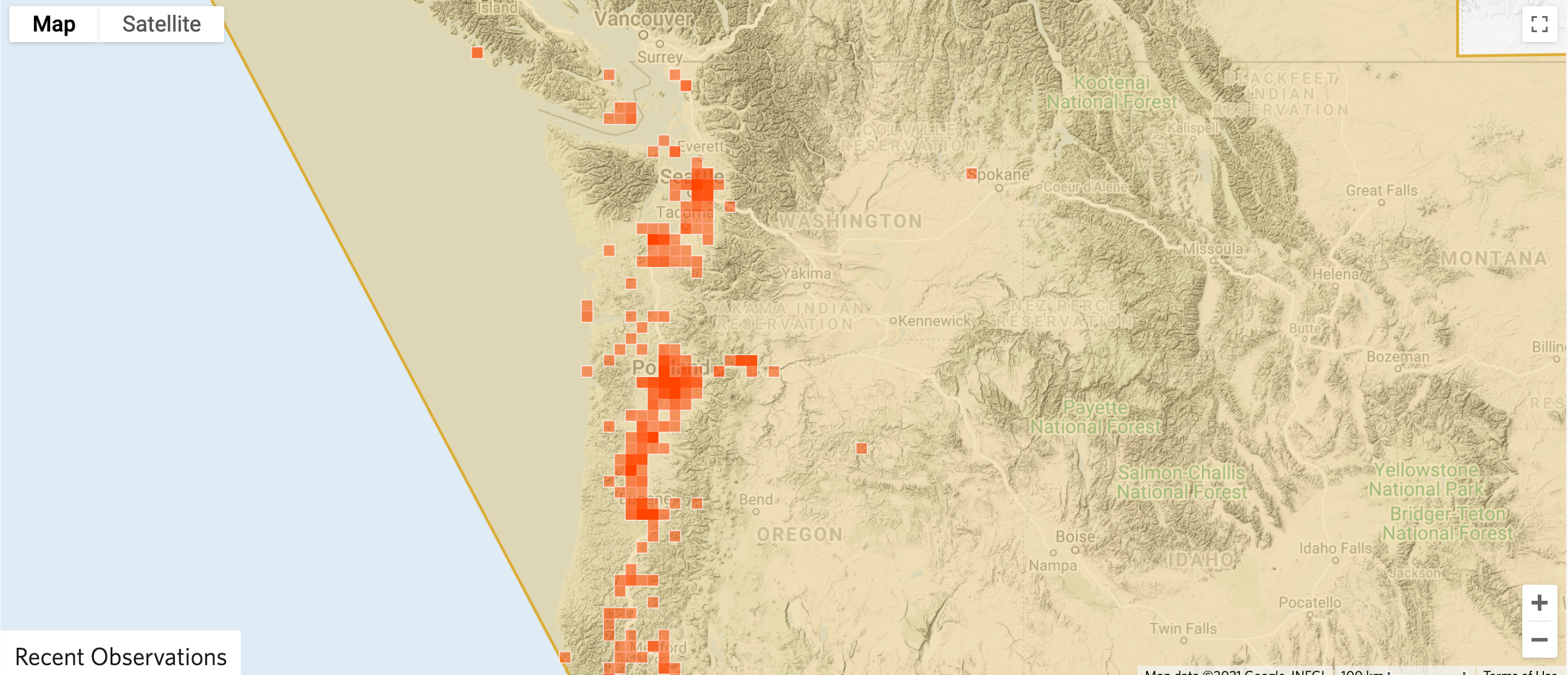
There are more than 1500 recorded observations of Oregon ash on iNaturalist. Explore this distribution to find an tree near you. Then, keep an eye on it for symptoms of EAB.
More information is available at the links below: